PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) is a microprocessor based device, which processes the
information received from the sensors according to the program and transmits it to the operational elements. PLC is an electronic system which operates based on the digital principles designed for using in an industrial environment. The system is aimed to control a machine or a process with the system’s own analog and/or digital input/output modules by using the functions of logical control, timing, counting, and arithmetical operations. Furthermore it ensures that device or process information is transferred to the SCADA environment.
One other application area of the PLC is to collect the production and process data related to the raw material. It may be related to the number and temperature of the product, processing time and any other measurable specification. The system design is primarily based on the correct definition of the need and selection of an optimum model. Any input/output which will be remained unemployed implies waste of money. Therefore the system designer is supposed to have all the necessary information.
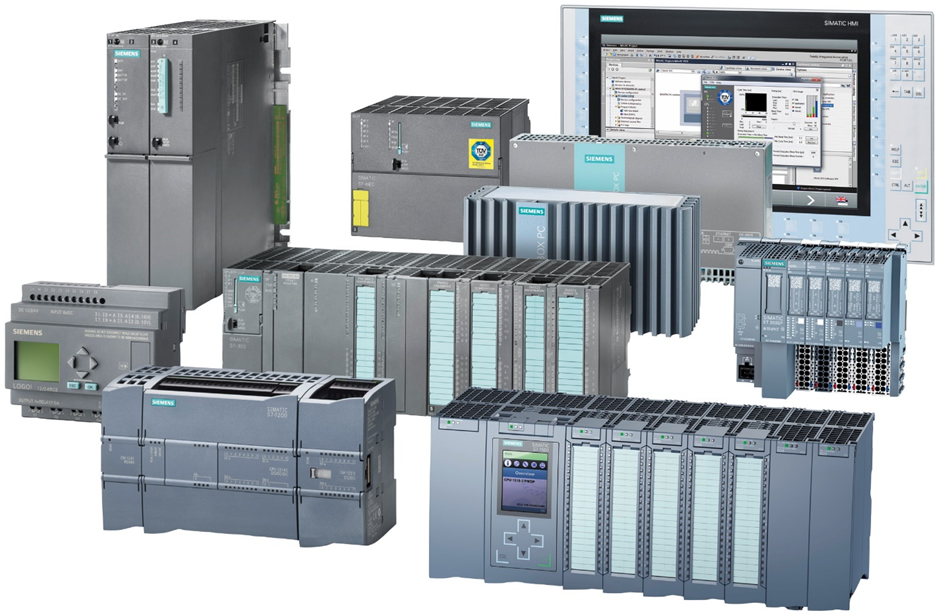
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) is microprocessor based devices used in automation systems and replace control elements such as auxiliary relays, time relays, counters. In these devices timing, counting, ordering and any kind of combined and successive logical operations are performed by using software. |
 |
|
|
|
In tis way, it is possible to solve complicated automation problems in fast and reliable manner. PLC systems:
- Simple and reliable.
- Low space and fewer breakdowns.
- Quick adaptability to new applications
- Not affected by adverse environmental conditions.
- Less cabling requirement
- Enable to utilize ready-for-use function.
- Inputs and outputs can be monitored |
 |
Some examples for applications performed via PLC,
Cement plants: Raw material provision, dosing systems, furnace control, and production automation.
Ceramic Industry: Raw material provision, recipe- based production, furnace control.
Food Industry: Recipe-based production.
Paper Industry: Power distribution control, production automation.
Chemical Industry: Recipe-based production control and automation.
Application areas of PLCs: |
1. Applications for Sequence Check |
|
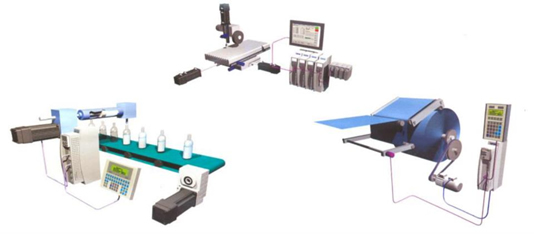 |
It ensures the works are to be performed in a defined sequence. For instance, to check at which and in which order an elevator should stop, to define the working sequence of machines in a production line. |
2. Applications for Motion Check |
|
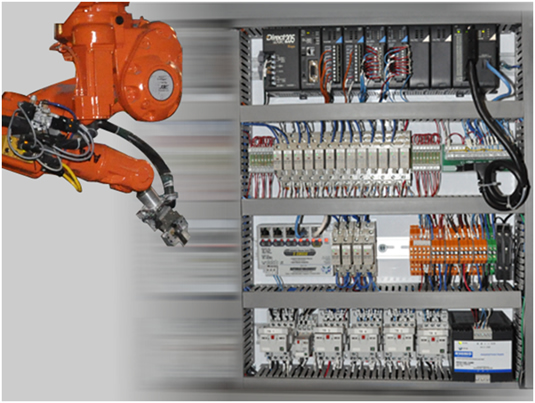 |
It is the integration of linear and rotational motion control systems to PLC. It may be a single or multi- axis system check, which can be utilized in servo, step or hydraulic drives. PLC applications for motion check are able to control infinite machine variety and multi axis motions, for example, Cartesian robots, film, rubber and nonwoven textile systems. |
3. Application for Process Control
This application is related to the control ability of PLC for several physical parameters (temperature, pressure, flow rate, speed, weight etc.). In turn, analog I/O (input/output) is required in order to create a closed-loop monitoring system. Thanks to utilization of PID software, PLC assumes the function of stand-alone loop monitoring devices. Other alternative is to combine the best features of both systems and to integrate PLC with control devices. Typical examples for this alternative are autoclave systems and heating furnaces. |
4. Application for Data Management4. Application for Data Management |
|
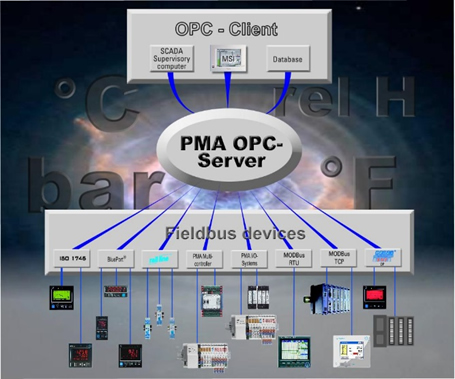 |
This application is used to collect data, which can be available in any process, to govern the processes as required, to collect information about the machineries and similar equipment, which are involved in the process, to compare the collected information with the reference data, to transmit them to any other device for investigating, monitoring and reporting. |
Main Units of PLC
Input Unit: Signal information from the sensors, such as pressure, level, and temperature regarding the system to be controlled is received via input unit.
Processing Unit: It is the main processing unit, which processes the information according to the program assigned itself and transmits the result as output information.
Output Unit: It processes the output data from the main processing unit according to a defined program, and then produces control signals required for the related monitoring operation.
Programming Unit: It is the unit, where the programs to be implemented by the processing unit are developed. Personal computers are frequently used for programming PLCs. |
|
Advantages of PLC
Reliability: It consists of electronic units which are protected against nearly all dangerous situations.
Physical Size: PLCs are space-saving devices comparing their capabilities. This, in turn, enables them to be used in every environment.
Cost: The initial cost of PLC solutions is very insignificant considering the initial cost and the production gain.
Resistance to Environmental Conditions: PLCs demonstrate a high level of resistance against environmental conditions as they are designed specifically for the industrial conditions.
Communication Capability: PLCs are able to communicate with each other, PCs and other smart devices.
Complex Structure: PLCs are able to perform the simultaneous control of many equipment by means of sub-programs assigned for each operational element in the memory.
Flexibility: PLC programs can be easily and quickly modified. Furthermore PLC memories are extendable.
Processing Speed: PLC can process any program which includes logical and arithmetical operations, in a very high speed.
Displaying: The operation of a circuit related to a PLC program can be directly monitored over the display. Furthermore failure scan can be made and past working status can be displayed subsequently.
|